Gardener seeking shrub. Must be drought tolerant. Must have year-round interest. Must be easy to grow and maintain. Preferably flowers in late summer or early fall. Must be attractive – not just to humans, but to wildlife as well. Serious inquiries only.
My answer to a solicitation such as this would be rabbitbrush. While there may be other perfectly acceptable plants that fit this description, I think rabbitbrush deserves major consideration. It’s easy to grow and can be kept looking attractive throughout the year. When it is flush with vibrant, golden-yellow flowers at the close of summer, it not only becomes the star of the garden visually, but also a savior to pollinators readying themselves for winter. Plus, it requires little to no supplemental water, making it a true dry garden plant.
There are many species that go by the common name rabbitbrush. The two that I am most familiar with are Ericameria nauseosa (rubber or gray rabbitbrush) and Chrysothamnus viscidiflorus (green or yellow rabbitbrush). Both of these species are native to western North America, and both have a number of naturally occurring varieties and subspecies.
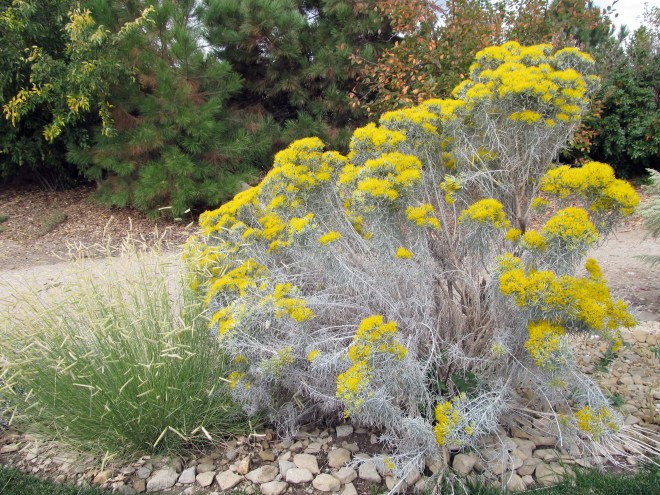
Rubber rabbitbrush is a densely branched shrub that reaches an average height of 3 feet. Its leaves are slender and numerous, and its stems and leaves are covered in short, white, felt-like hairs giving the plant a light gray appearance. Native Americans used the flexible branches of this plant to weave baskets. They also made a tea from the stems to treat coughs, colds, chest pains, and toothaches. Bundles of branches were burned to smoke animal hides. The stems and roots contain a latex sap, and certain Native American tribes are said to have used this sap as chewing gum, possibly to relieve hunger or thirst. A rubber shortage during World War II led to investigations into extracting the latex from rabbitbrush. This idea was soon abandoned once it was determined that even if every rabbitbrush in the West were to be harvested, the resulting increase in rubber would be modest compared to other sources.
Green rabbitbrush is typically smaller than rubber rabbitbrush, reaching a maximum height of about 3 feet. Its stems and leaves appear similar to rubber rabbitbrush except they lack the dense, white hairs and are brown and green respectively. Also, the stems and leaves of green rabbitbrush have a stickiness to them, and the leaves are often twisted or curled.
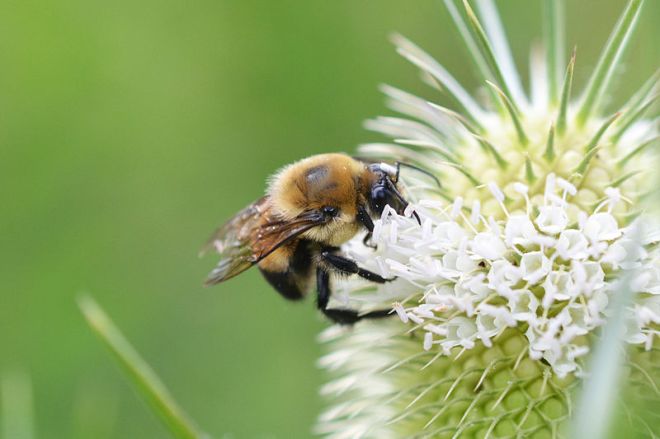
Rabbitbrush is a member of the sunflower family (Asteraceae). Plants in this family generally have inflorescences that are a combination of ray and disk flowers (or florets) clustered tightly together and arranged in such a way that the inflorescence appears as a single flower. Consider sunflowers, for example. What appear to be petals around the outside of a large flower are actually a series of individual ray flowers, and in the center are dozens of disk flowers. Both rubber and green rabbitbrush lack ray flowers, and instead their inflorescences are clusters of 5 or so disk flowers that are borne at the tips of each branch creating a sheet of yellow-gold flowers that covers the shrub. Native Americans used these flowers to make dyes.
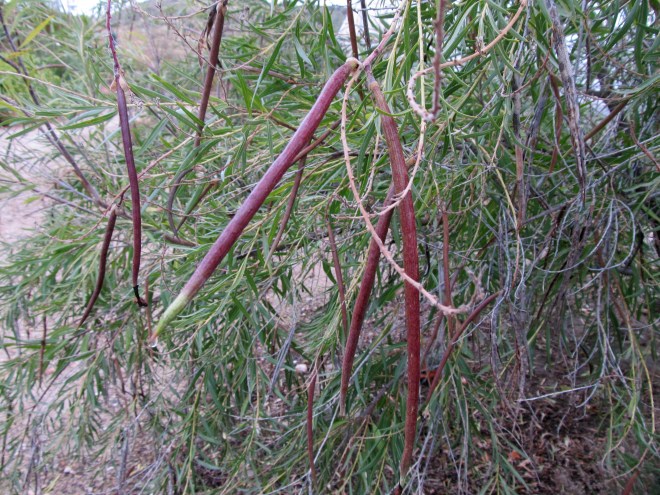
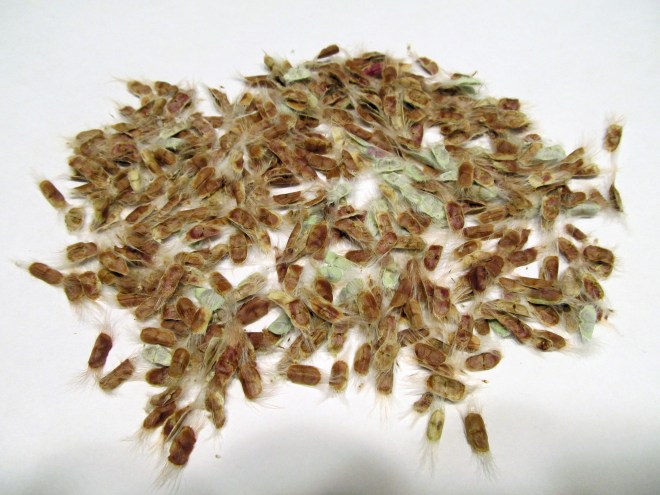
The fruits of rabbitbrush are achenes with small tufts of hairs attached. Each achene contains one seed. The tuft of hair (or pappus) helps disseminate the seed by way of the wind. Many of the fruits remain attached to the plant throughout the winter, providing winter interest and food for birds.
As rabbitbrush ages it can become gangly, floppy, or simply too large for the site. This can be avoided easily by cutting the plant back by a third or more each fall or spring, which will result in a more manageable form. It can also be cut back nearly to the ground if it is getting too big.
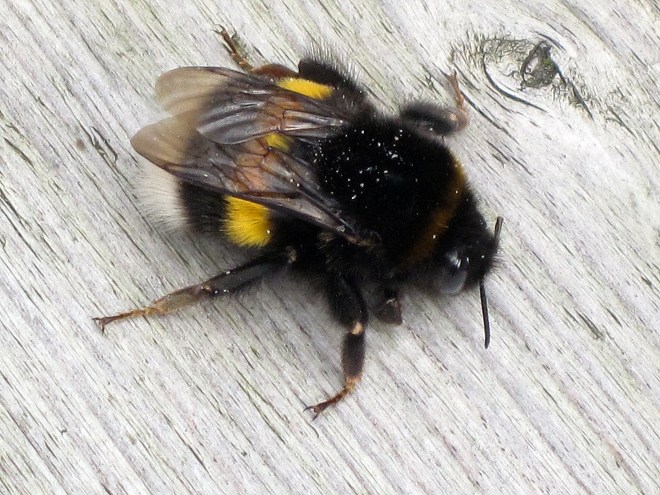
The leaves, flowers, stems, and seeds provide food for a variety of animals including birds, deer, and small mammals. The plant itself can also provide cover for small mammals and birds. Oh, and did I mention that it’s a pollinator magnet. It has wildlife value, it’s drought tolerant, it’s easy to maintain, and overall, it’s a beautiful plant. What more could you ask for in a shrub?
More Drought Tolerant Plant posts at Awkward Botany:
–Water Efficient Landscape at Idaho State Capitol Building
The photos in this post were taken at Idaho Botanical Garden in Boise, Idaho.