The aster family has a lot to offer. It’s really no surprise considering that Asteraceae is the largest family of flowering plants in the world with as many as 33,000 species. Certainly its ecological importance is substantial. It also contains, arguably, some of the most beautiful and attractive plant species, as well as a significant selection of useful plants from a human perspective. When a plant family is this big, it is essential to subdivide it into smaller groups in order to better understand it. The subject of this post finds itself in a tribe within the aster family called the thoroughwort tribe or Eupatorieae – home to other familiar genera like Ageratina, Ageratum, Eupatorium, Eutrochium, Conoclinum, and Stevia.
Liatris is a North American genus that includes around 37 species and at least 12 naturally occurring hybrids. All of these species are found east of the Rocky Mountains – scattered across the Midwest, in the northeastern and southeastern regions of the United States, as well as north into Canada and south into Mexico. While there are a couple of species found within the Rocky Mountain region, there are no species of Liatris found west of the Rockies. One species is found in the Bahamas.
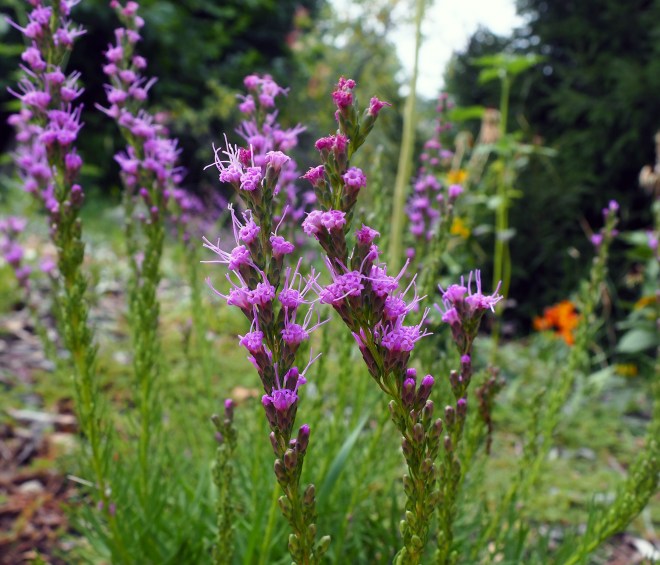
Commonly known as gayfeathers or blazing stars (not to be confused with the blazing stars of the Mentzelia genus in the family Loasaceae), Liatris is a group of perennial plants with upright, mainly unbranched stems that flower from the summer into the fall. After dying back to the ground in the winter, they emerge in the spring from elongated or globular corms, their narrow leaves giving the appearance of a tuft of grass. Flowers occur in the upper portions of upright stems and are held in bell-shaped or cylindrical involucres. They lack ray florets like those of a typical aster flower. Instead, each flower is composed only of a series of small disc florets which can give them a button-like appearance. Flowers come in shades of lavender, magenta, pink-purple, and rose-purple (sometimes white).
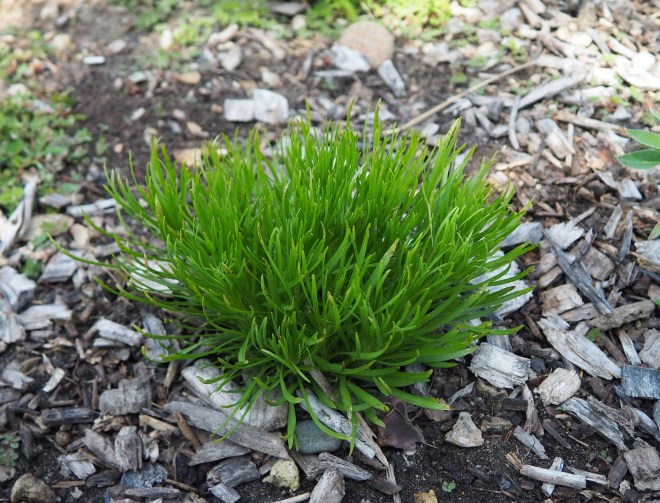
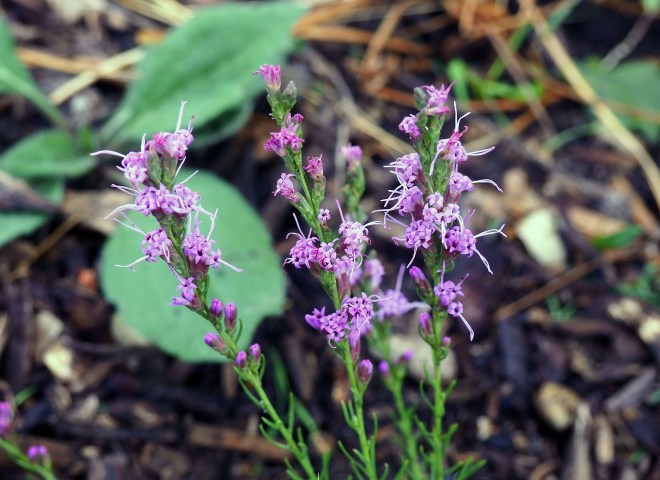
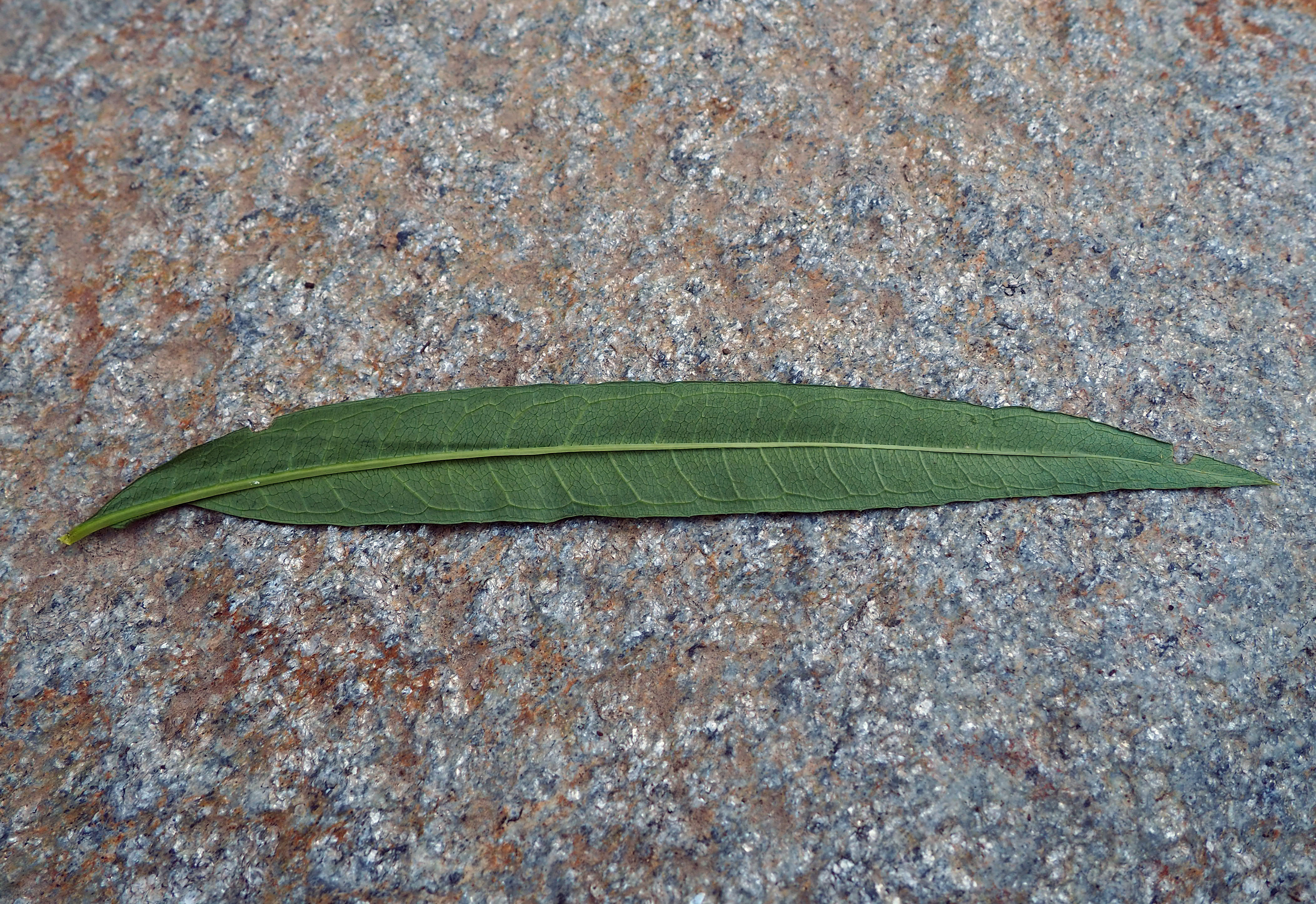
Plants in this genus vary in height, with the tallest reaching over 5 feet. My affinity for diminutive plants draws me to some of the shorter plants in this group, particularly Liatris microcephala or smallhead blazing star. Other common names for this plant include dwarf blazing star and Appalachian blazing star. This species has very slender, linear leaves and looks a lot like a little bunchgrass for much of the growing season until its flower stalks start to emerge in midsummer. These stems can rise to 2 feet tall or more, but are often much shorter, especially in the lean soils that I grow them in here in Idaho. Linear leaves lacking petioles are alternately arranged along the length of the flowering stems. Flowers are rose-purple or lavender and composed of only 4 to 6 disc florets. They flank the upper portion of the upright stems, and gradually open from the top down from mid to late summer into the fall.
The fruits of Liatris are slender, ribbed achenes with a short, bristly pappus attached that is either feathery or barbed. The pappus of L. microcephala is minute and bristly. Once mature, the fruits detach from the plant and are blown around by the wind, sometimes grabbing on to the fur of passing animals.
L. microcephala has a relatively limited natural distribution, occuring mainly in the southern Appalachian Mountains from western North Carolina and Kentucky, south to western South Carolina, north and central Georgia, and into northern Alabama. It prefers dry, rocky, slightly acidic soils, but can tolerate other soil types as long as they are well-drained. It prefers full sun and tolerates high heat and humidity. Its tendency to grow in rocky outcrops makes it a good rock garden plant. It is also used on green roofs. Like most other plants in this genus, L. microcephala needs well-draining soils particularly during the winter, as corms can rot out when they stay wet over prolonged periods.
A Chicago Botanic Garden plant evaluation report includes Liatris in a list of perennials that first gained popularity in European gardens before finding favor in the North American horticulture industry. In spite of being native to North America, gardeners on this continent looked to plants from other parts of the world to fill their gardens. Now, as trends shift towards native plants and habitat gardens, plants like native blazing stars which are visited by a variety of insect species and whose seeds are consumed by birds, are an obvious choice. They are relatively easy to grow and care for, and there is a wide selection to choose from, including cultivars. Though not native to the west, blazing stars are great plants for gardens in our region due to the drought-tolerance that is common in this group. Water conservation is of particular importance in the semi-arid west, and L. microcephala, with its penchant for growing on rocky outcrops is particularly drought tolerant. Apart from that, it’s just a beautiful, little plant and one that I will continue to grow, with the dream of someday seeing it in its natural setting.