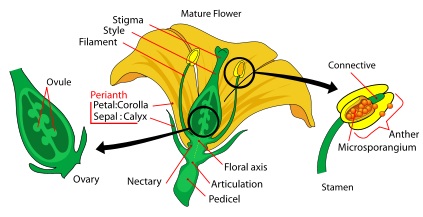
“The stage is set for reproduction when, by one means or another, compatible pollen comes to rest on a flower’s stigma. Of the two cells within a pollen grain, one is destined to grow into a long tube, a pollen tube, that penetrates the pistil’s tissues in search of a microscopic opening in one of the ovules, located in the ovary. … The second of a pollen grain’s cells divides to become two sperm that move through the pollen tube and enter the ovule.” – Brian Capon, Botany for Gardeners
“Once pollination occurs, the next step is fertilization. Pollen deposited on the sticky stigma generates a fine pollen tube that conveys the sperm through the style to the ovary, where the ovules, or eggs, have developed. After fertilization, the rest of the flower parts wither and are shed as the ovary swells with seed development.” – Rick Imes, The Practical Botanist
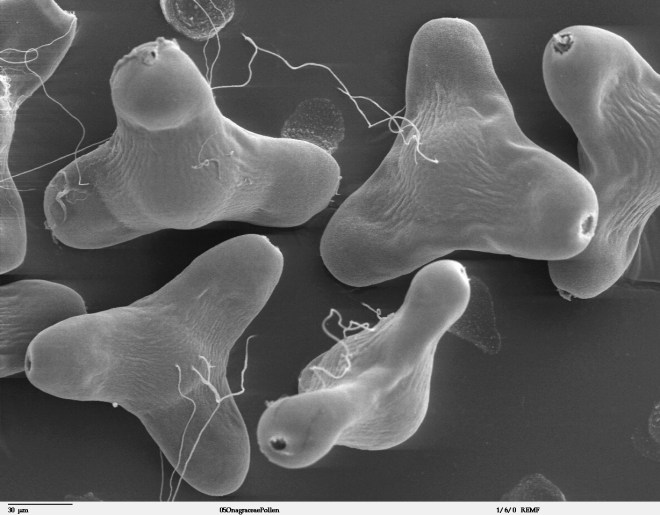
Pollination tells the story of a pollen grain leaving an anther by some means – be it wind, water, or animal – and finding itself deposited atop a stigma. As long as the pollen and stigma are compatible, the sex act proceeds. In other words, the pollen grain germinates. One of the pollen grain’s cells – the tube nucleus – grows down the length of the style, forming a tube through which two sperm nuclei can travel. The sperm nuclei enter the ovary and then, by way of a micropyle, enter an ovule. Inside the ovule is the female gametophyte (also referred to as the embryo sac). One sperm nucleus unites with the egg nucleus to form a zygote. The remaining sperm nucleus unites with two polar nuclei to form a triploid cell which becomes the endosperm. The sex act is complete.

The illustration on the left includes the cross section of a pistil showing the inside of the ovary where pollen tubes have made their way to the ovules. The illustration on the right shows pollen grains germinating on a stigma and pollen tubes as they work their way down the style. (image credit: wikimedia commons)
The zygote divides by mitosis to become an embryo. The endosperm nourishes the development of the embryo. The ovule matures into a seed, and the ovary develops into a fruit. During this process, the remaining parts of the flower wither and fall away. In some cases, certain flower parts remain attached to the fruit or become part of the fruit. The flesh of an apple, for example, is formed from the carpels and the receptacle (the thickened end of a flower stem – peduncle – to which the parts of a flower are attached).
As the seed matures, the endosperm is either used up or persists to help nourish the embryonic plant after germination. Mature seeds that are abundant in endosperm are called albuminous. Examples include wheat, corn, and other grasses and grains. Mature seeds with endosperm that is either highly reduced or absent are called exalbuminous – beans and peas, for example. Certain species – like orchids – do not produce endosperm at all.
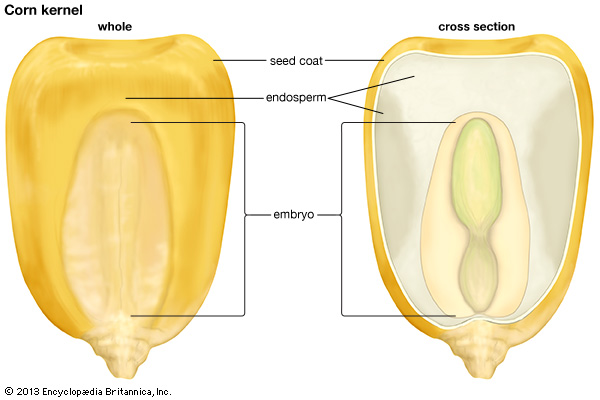
The cross section of a corn kernel showing the endosperm and the embryo (image credit: Encyclopedia Britannica Kids)
It is fascinating to consider that virtually every seed we encounter is the result of a single pollen grain making its way from an anther to a stigma, growing a narrow tube down a style, and fertilizing a single ovule. [Of course there are always exceptions. Some plants can produce seeds asexually. See apomixis.] Think of this the next time you are eating corn on the cob or popcorn – each kernel is a single seed – or slicing open a pomegranate to reveal the hundreds of juicy seeds inside. Or better yet, when you are eating the flesh or drinking the milk of a coconut. You are enjoying the solid and liquid endosperm of one very large seed.
Much more can be said about pollination and the events surrounding it, but we’ll save that for future posts. The “Year of Pollination” may be coming to an end, but there remains much to discover and report concerning the subject. For now, here is a fun video to help us review what we’ve learned so far:
Also, take a look at this TED talk: The Hidden Beauty of Pollination by Louie Schwartzberg
And finally, just as the “Year of Pollination” was coming to an end I was introduced to a superb blog called The Amateur Anthecologist. Not only did it teach me that “anthecology” is a term synonymous with pollination biology, it has a great series of posts called “A Year of Pollinators” that showcases photographs and information that the author has collected for various groups of pollinators over the past year. The series includes posts about Bees, Wasps, Moths and Butterflies, Flies, and Beetles, Bugs, and Spiders.